Cervical osteochondrosis is a progressive dystrophic-degenerative lesion of the intervertebral discs in the region of 1-7 vertebrae belonging to the cervical spine.
As a consequence of cervical osteochondrosis, deformation, exhaustion, and then damage to the vertebral body occur. This disrupts the normal blood supply and nerve conduction in the neck and in those areas innervated by the nerve roots of the cervical spine.
Cervical osteochondrosis can be isolated or combined with osteochondrosis of other parts - thoracic, lumbar and sacral.
Causes
It differs in the factors that predispose to the development of osteochondrosis. This includes:
- sedentary and sedentary lifestyle;
- sedentary types of work with static load on the neck;
- overweight, insufficient physical development;
- connective tissue dysplastic processes;
- circulatory disorders in the neck;
- neck injuries;
- scoliosis, poor posture, uncomfortable pillows and mattresses;
- hereditary predisposition, metabolic defects.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis. Complications
The cervical spine is most susceptible to the development of osteochondrosis. The vertebrae are the smallest in it in relation to other parts of the spine, the muscular frame is not very pronounced, the vertebrae are affected by the weight of the head and the upright posture. In the cervical spine, the vertebrae fit tightly together. Even a minimal change in them can lead to compression and even displacement of nerves and blood vessels.
The most characteristic symptom that patients complain of is pain in the cervical spine. Depending on the affected area, the pain can be localized: in the collarbone and shoulder; all over the cervical spine; on the anterior surface of the thorax.
The first signs of cervical osteochondrosis may be insignificant: a feeling of heaviness in the head, headache in the occipital region, neck pain in the evening, a feeling of numbness or tingling in the shoulders and arms.
Leading symptoms
Vegetative-dystonic.
Strong "shooting" pain in the neck, in the area just below the nape of the neck. The pain occurs after a long stay in one position, after sleeping, constant tension of the neck muscles.
Difficulty moving the hand to the side, numbness, numbness of the fingers. Due to the compression of the vertebral arteries, neurological manifestations are observed: headache, nausea, dizziness, unreasonable jumps in blood pressure.
Spinal symptom.
The pain is localized behind the sternum on the left.
This type of pain should be distinguished from angina pectoris (in angina pectoris nitroglycerin brings relief, in osteochondrosis it does not).
Gradual disruption of the structure of the intervertebral discs leads to their compression and injury of the nerve roots, as well as narrowing or involvement of the arteries and veins that pass in the area of the vertebral body.
This leads to the creation of special syndromes - radicular and ischemic:
- defeat of the root of the first cervical vertebra (C1): abnormalities in the occiput;
- C2 lesion gives pain in the area of the scalp and nape;
- lesion C3 gives neck pain on the side of the injury, decreased sensitivity in the tongue and hypoglossal muscles, speech impairment is possible;
- damage to C4 and C5 results in shoulder and collarbone pain, decreased head and neck muscle tone, hiccups, respiratory distress, and heart pain;
- C6 lesion occurs most often, gives pain from the neck to the shoulder blades, forearms, to the thumbs, skin sensitivity may suffer;
- C7 lesion - similar symptoms with pain in the neck, back of the shoulder, to the back of the hand, decreased arm strength and decreased reflexes.
Circulatory disorders due to compression of blood vessels in the cervical vertebrae can lead to headaches, migraines, dizziness, visual impairment and tinnitus, flashes of flies in front of the eyes, and disorders of autonomic functions.
Manifestations of heart syndrome can occur with pressing pain in the heart, lack of air and palpitations, rhythm disorders.
Complications.
Protrusion of intervertebral discs with hernia formation (protrusion).
Rupture of the intervertebral disc with pinching of nerves and blood vessels, possible compression of the spinal cord, which can be fatal.
Root lesions (radiculopathy), the formation of spines on the bodies of the vertebrae (osteophytes) with the manifestation of paresis and paralysis.
In case of the above problems, it is necessary to contact an orthopedist or neurologist, and conduct the necessary research.
Nutrition
Proper nutrition will significantly alleviate the condition of osteochondrosis. The diet should be complete. If a person has a normal body weight, then as a basis you can take therapeutic diet number 15 according to Pevzner. It contains all the necessary minerals and an increased amount of fat and water-soluble vitamins. It is necessary to eat food rich in natural chondroprotectors. Chondroitin is found in red fish, animal tendons and cartilage, and chicken.
Be sure to take clean water in a volume of 1, 5-2 liters. Fluid is needed to prevent the intervertebral discs from drying out.
Traditional and non-traditional treatments
Treatment
Today, there are both traditional and non-traditional methods of treating osteochondrosis in the cervical spine.
Drug treatment methods: symptomatic analgesic therapy to relieve pain; taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve inflammation and tissue edema; antispasmodics; drugs to improve blood circulation; chondroprotectors to restore the structure of intervertebral discs.
The course of therapy with vitamin B group, external means for therapy - gels and ointments, creams with anti-inflammatory, warming and analgesic components are presented.
During the period of exacerbation, it is recommended to wear a special necklace (Shants collar).
Complications of cervical osteochondrosis with intervertebral hernias that impair sensitivity and blood circulation can be treated quickly.
The duration of treatment depends on neglect of the condition, as osteochondrosis is a progressive chronic disease. Treatment can be long, and preventive courses can be carried out for life.
Physiotherapy treatments.
These include exercise therapy, magnetotherapy, balneotherapy, laser therapy, acupuncture, Ljapko's application therapy and massage.
Physiotherapy
It is necessary to do exercises for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis several times a day every day. They include self-stretching, self-massage, a set of special exercises. Avoid neck injuries and lifting loads.
It is necessary to combine long-term sitting with periods of rest and warm-up.
The basis of cervical spine health is a strong and healthy back, physical activity, a comfortable bed with anatomical pillows and a mattress, proper posture and proper nutrition.
Therapy using Lyapko
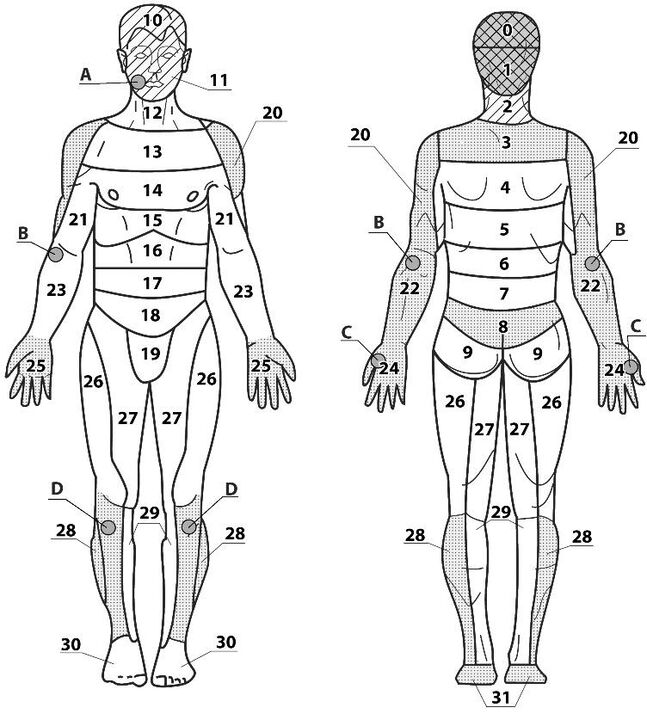
Areas of application:
- basic 2, 3;
- additional 1, 4, 12, 13;
- auxiliary 20, 22, 28, 31.
General recommendations
When using the applicator, the main, additional and maximum pain zones are used, but in case of severe pain, the applicators should be applied above and below the painful zone or use points and zones on the opposite side. Exposure time 10-30 minutes.
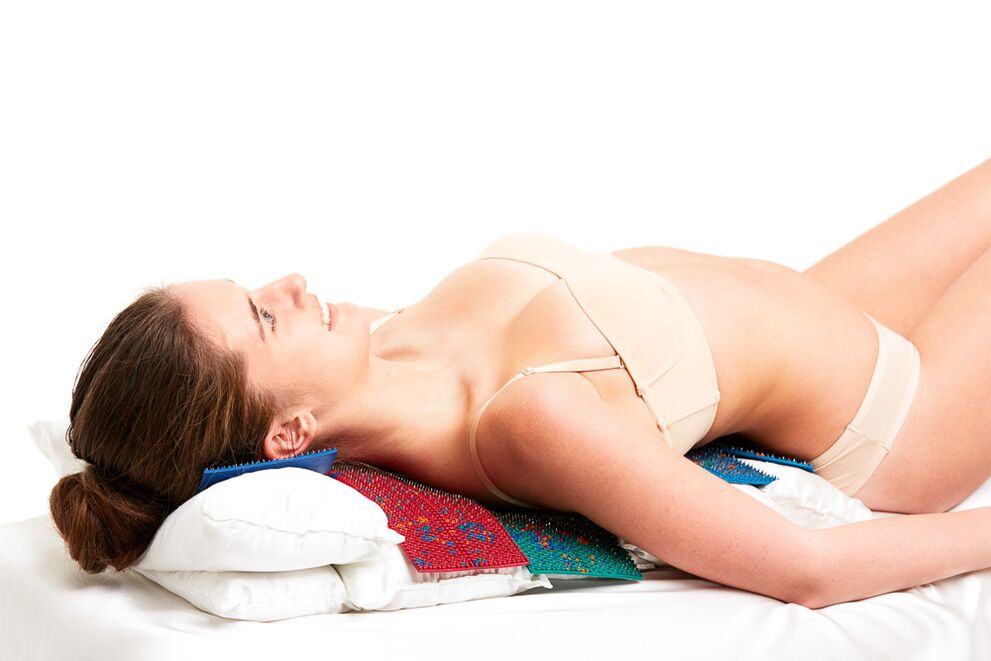

If cervical osteochondrosis is combined with osteochondrosis of other parts - thoracic, lumbar and sacral, then application therapy can be applied simultaneously or alternately to all parts of the spine. The larger the exposure area, the better the effect.















































